
What is “good control”?
Where should I look when evaluating control?
To answer these questions, this page describes the basic control performance evaluation criteria.
Control performance should be evaluated based on the followings.
- Stability
- Tracking Accuracy
- Response Speed
- Overshoot/Undershoot
- Sensitivity to Disturbances
- Sensitivity to Characteristic Changes
Criterion 1: Stability
In a nutshell, a system is stable when its output converges.

Of course, this is the most basic performance of a control system. However, it can be difficult to achieve if a control target is essentially unstable.

Note: For more details on system stability, please see this page:
Criterion 2: Tracking Accuracy
It is also important that an output (controlled variable) tracks a reference with good accuracy.
Note that a controller that has not been designed correctly can produce a steady-state error, where the output cannot reach the reference forever, as shown below.
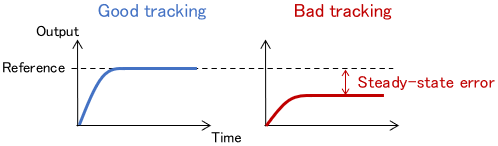

Criterion 3: Response Speed
Quick response to changes in reference is another important performance criterion. No matter how good the final tracking accuracy is, it is meaningless if it takes a huge time to reach it.
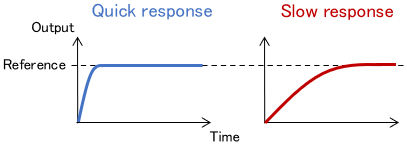

Some textbooks introduce the following indicators of response speed.
- Rise time: Time required for the step response to reach 90% of its steady-state value from 10%.
- Delay time: Time required for the step response to reach 50% of its steady-state value.
- Peak time: Time required for the response to reach its first peak.
- Settling time: Time until the response settles within ±2% of the steady-state value
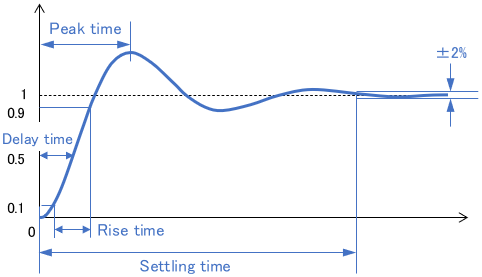

It is important to know the concept of each term, but there is little need to memorize numerical values such as “to reach XX%.” In practical situations, how and where to check varies depending on the system.
For example, in manufacturing, critical parts of an operation vary depending on the product. Therefore, the focus should be subject to change (i.e. flexible) according to the target.


Criterion 4: Overshoot/Undershoot
If a controller is improperly designed, overshoot or undershoot may occur as follows:


No matter how good the tracking accuracy and response speed are, the performance would be unpleasant if the controller takes three steps forward and two steps backward. It is important to prevent such behavior.
Criterion 5: Sensitivity to Disturbances
Real systems are basically subject to unexpected disturbances. A system greatly affected by disturbances is said to have high sensitivity to disturbances, and vice versa.
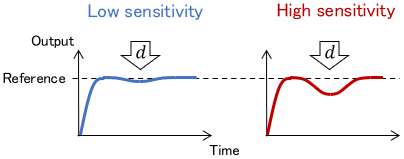

When designing a control system, it is important to construct a system that can tolerate a certain amount of disturbance (i.e. low sensitivity to disturbance).
Criterion 6: Sensitivity to Characteristic Changes
System characteristics often change due to changes in operating conditions or aging. As with disturbances, the degree of influence is referred to as high (or low) sensitivity to characteristic changes.
Naturally, it is best to construct a system with low sensitivity to characteristic changes.
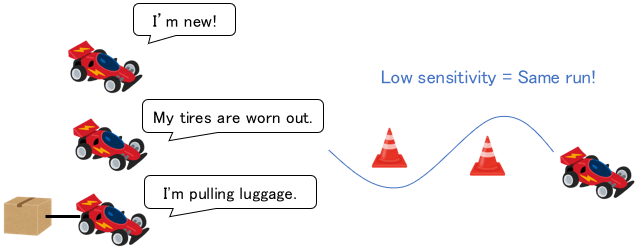

The above is the basic control performance evaluation criteria. It can be difficult to satisfy all of them. Therefore, in practice, it is often necessary to discard and select the performance to be satisfied depending on the system.
Control performance should be evaluated based on the followings.
- Stability
- Tracking Accuracy
- Response Speed
- Overshoot/Undershoot
- Sensitivity to Disturbances
- Sensitivity to Characteristic Changes



Comments